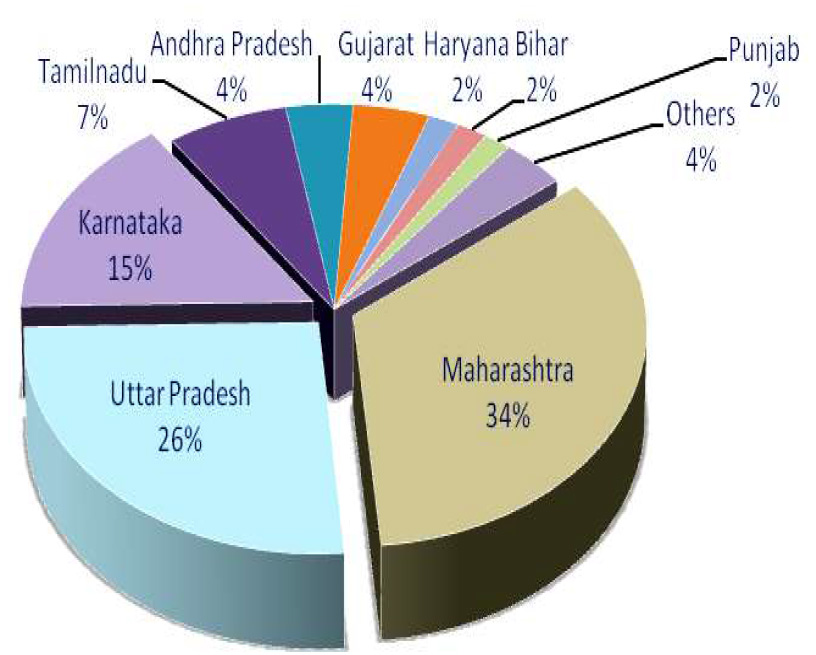
Cost of Project and Means of Finance

In First Year
Industry Overview
The Integrated Ethanol Complex has got Huge Potential as all the Products like Sugar Ethanol & all by products like BIOCNG & Fertilizers has got definitive & Lucrative Market.

As Indian Government has introduced many favourable Policies to Boost the Business. And Ethanol, BIO-CNG are purchased through Advanced & Fixed Rate Agreements by IOCL (Indian Oil Company Ltd.) There are Greater hopes of furthers Enrichment in Ethanol Sector as Indian government has decided to go with 100% Green Energy till 2050 & considering the current total requirement of Fossil fuel in India of 3500 CRORE litres from which we have only reached up to 3.8% of the total requirement that is 1,200 CRORE Litres. As per global Energy experts this industry is likely to Boom for another 20 Years.
- We will be using defuses instead of mills for extraction of juice from the sugar cane where we will have almost 17-18 % more sugar extraction than the traditional method of milling.
- We will be diverting almost 100%of juice to ethanol which will result in maximum production of ethanol than the traditional plant having hybrid system where part of he juice is diverted for sugar production and part is diverted for ethanol production which will definitely enhance profitability in the project.
- We have planned another unique technology which is newly introduced in Industry is MVR i.e., Mechanical Vapour recompression system which will save around 30-40% energy for making syrup from Juice Additionally, we will be also getting our distillery (Ethanol) Section designed on 1.5 kg pressure instead of traditionally distillery on 3.5 kg pressure and the steam will be derived from reverse vapours from MVR which vapours otherwise goes waste, hence we will not only use vapour going waste but we will save at least 30 TPH boiler capacity to produce those vapours which will definitely enhance profitability in the project we have planned.
- Will be also using the spaint wash generated during process of ethanol formation for production of biogas by installing bio digesters in the same plant Even in the same plant we will additionally install another bio digester to digest press mud for formation of Mythen. Here in traditional plant spaint wash is burn in the incineration boiler as it is bio hazardous material. The generated bio gas will be further purified and compressed to use for automobiles as bio CNG and solid waste generated from this plant will be sent to the spray dryer which is also unique and newly invented technology where we will get potash rich bio fertilizers. And the liquid waste generated from this plant will be send to STP plant where the final discharge will be use for irrigation of Farm land which can be sold to farmers In this complete process we will have the most environment friendly plant as well as most production where will get substantial financial profitability by selling bio CNG potash rich fertilizers and water.
In the ethanol section we will be also making plant compatible for multifeed distillery hence the plant will be compatible to run on its own grains because of this unique design we will be able to run the plant round the year means almost for more than 330 days in total because of this feature with nominal additional investment and almost same overhead we will be able to increase profitability by almost 70-80% As we explained this will be first plant in India having all features in single plant
Our USP
Junnar Sugars Limited Pune is located in one of the progressive sugar belts in Western Maharashtra at Junnar Sugars Limited Pune. The command area of the proposed sugar plant reportedly has adequate irrigation facilities & potential for sustained cane supply to the sugar mill. The Location of Sugar Factory is so Unique & Ideal Considering the required Sugarcane Availability in the Vicinity of 5 kms & also Quite Convenient for Commuting as its just 7 kms from National Highway But still isolated in the lap of Mountain.
Industry Size, Structure and State wise Production Trends:
The ISI accounted for more than 15% of the total world sugar production in the last 5 years ending SS22-23. As of January 31, 2023, India had 683 sugar mills (including two standalone refineries) with a major concentration in rural areas. About 50% of the sugar mills are promoted by sugarcane farmers in the form of cooperative societies (refer to Table 1 for the breakup of sugar mills on the basis of ownership structure)
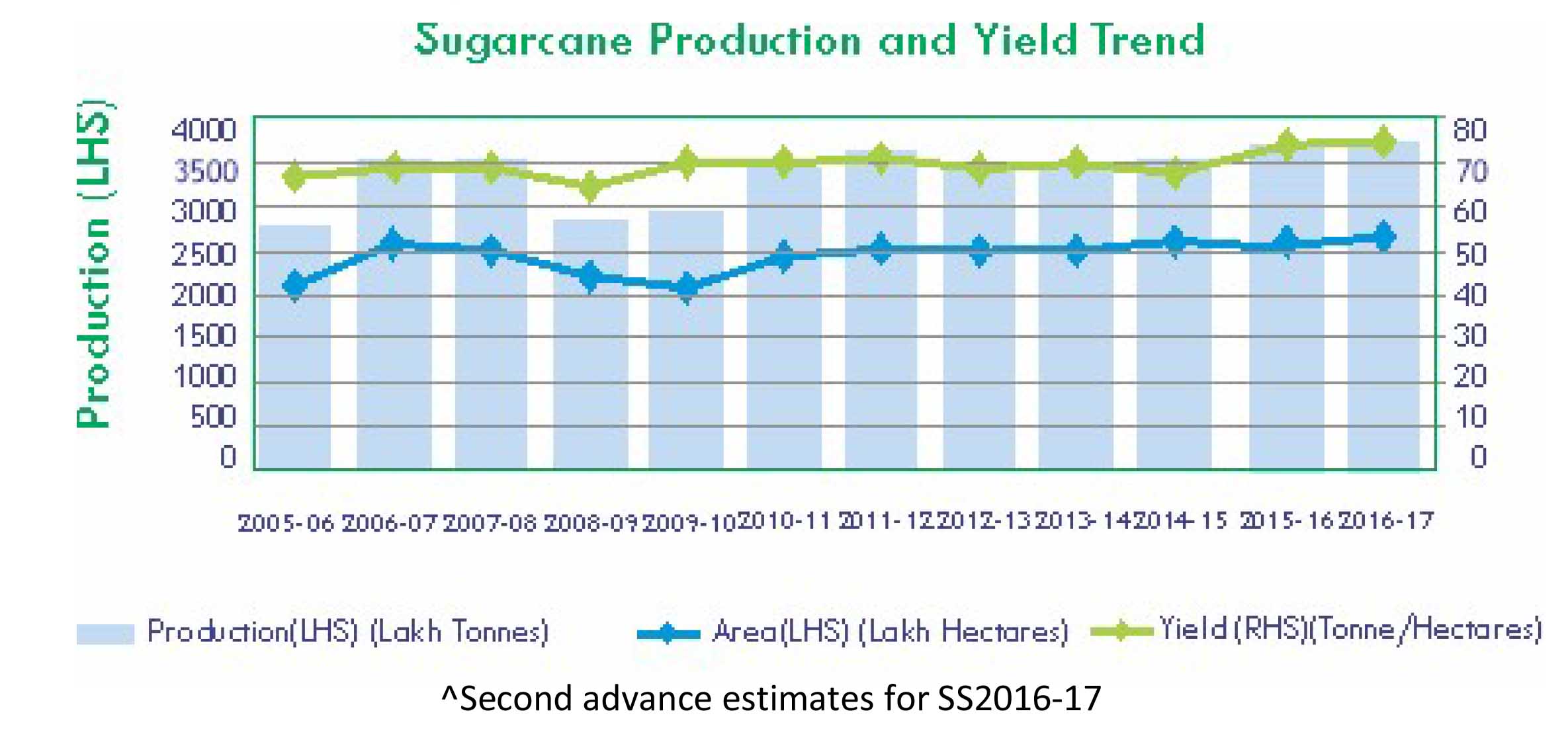
Chart 1: Sugarcane acreage, Production and yield in India
Source: Department of Food & Public Distribution (for Sugarcane Production) and Agricultural Statistics (for production and area of Sugarcane)
328 units have distillery facility, while 210 have own cogeneration power plants. India produces around 300-350 MMT sugarcane, 24-26 MMT white sugar and 6-8 MMT jaggery and khandsari annually to meet the demand for sweeteners. Moreover, the ISI produces about 2,700 million litres of alcohol, 2,300 Mega Watt (MW) of power and multiple allied products. The industry exports about 1,000 MW of power to grid after meeting its captive power requirement. ISI is gradually transforming into sugar complexes by producing sugar, bio-electricity, bio-ethanol, bio-manures & chemicals, contributing about 1% to the national GDP. Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh (UP) and Karnataka are the major sugar producing states in the country.
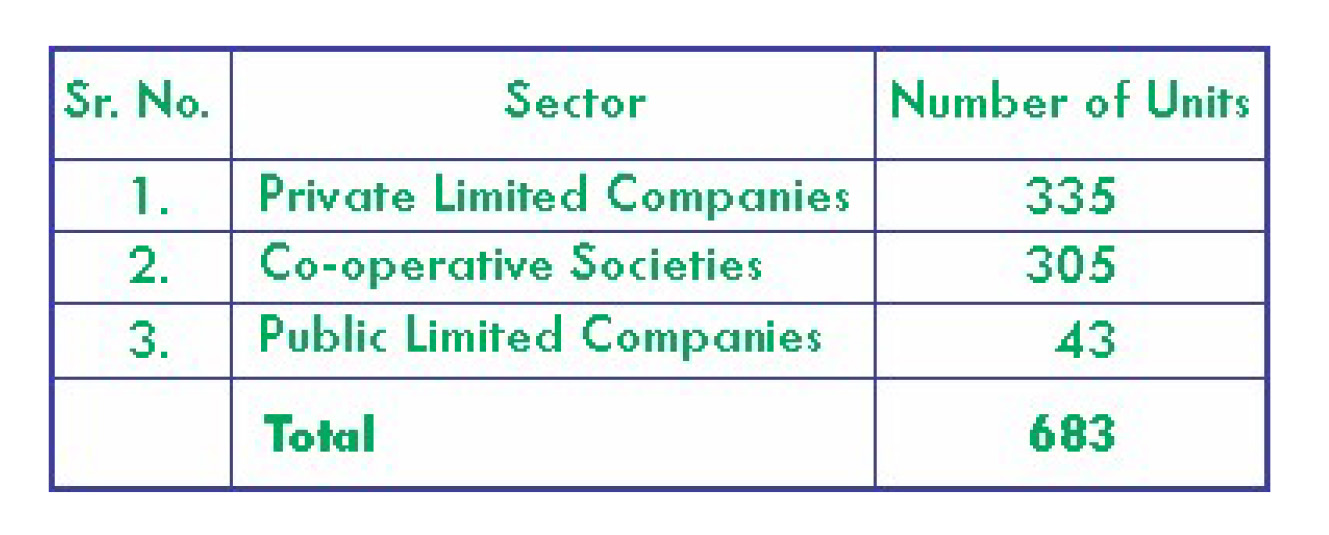
Table 1: Sugar mills in India
(Segregated on the basis of ownership structure)
Table 1: State-wise sugar production from SS10 to SS16.
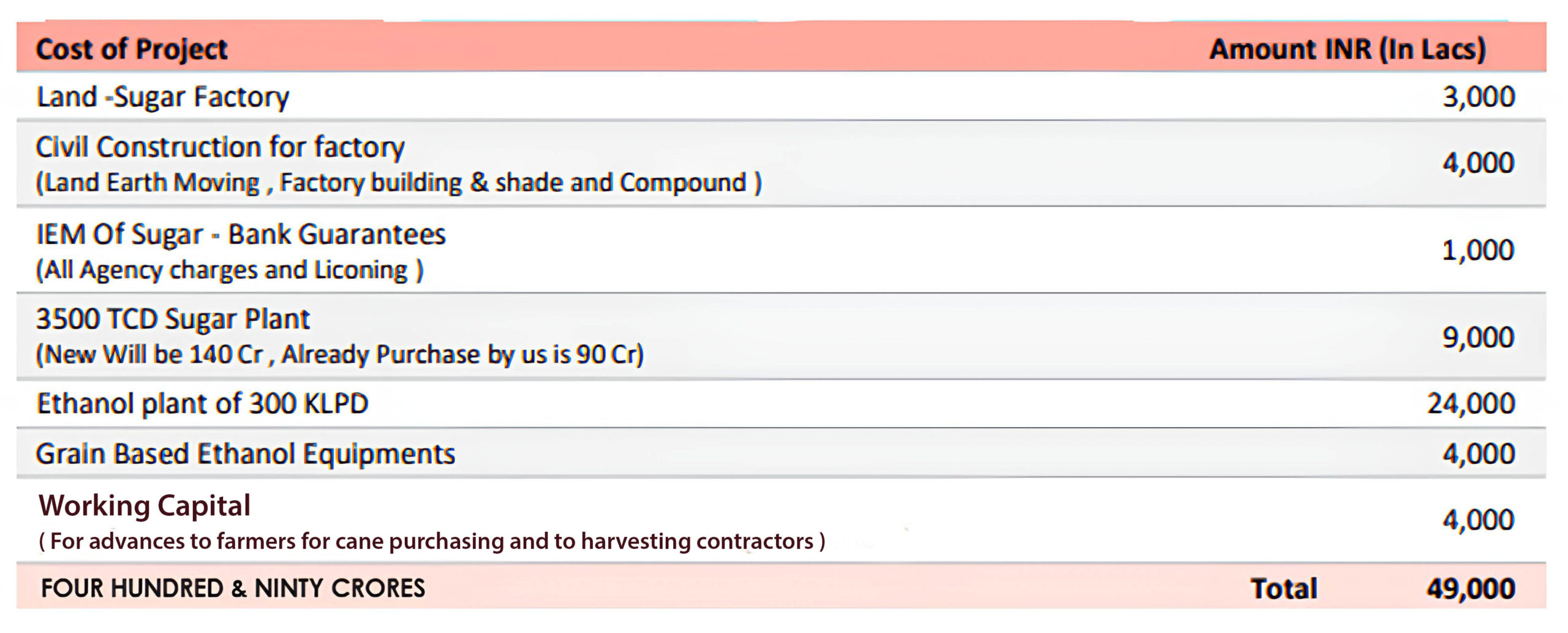
The top six states mentioned above account for approximately 90% of total India’s sugar production; of which Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh together account for nearly 60% of Total sugar production (refer to Chart 2 above for state-wise percentage production).
Uttar Pradesh was the largest sugarcane cultivating state and accounted for approximately 39% of the total sugarcane crop in SS15-16 followed by Maharashtra with 22%. The average yield of sugarcane during the last 5 years in UP was 57-59 tonne/hectare as compared with Maharashtra, which has an average yield of 80-85 tonne/hectare. Furthermore, UP also had a low sugar recovery rate and consequently ranked second in sugar production after Maharashtra during the last 5 years ended SS15-16.
The ISI is amongst the few industries that have successfully contributed to the rural economy. Furthermore, the farmers opt for sugarcane as a preferred crop on account of better yield per hectare, lower irrigation requirement, and strong intervention by the government towards the protection of the interest of the farmers in terms of the price of cane through FRP / SAP.